house has multible steps, whats best way to carry items up
The internet of things, or IoT, is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-calculator interaction.
A thing in the internet of things can be a person with a heart monitor implant, a subcontract animal with a biochip transponder, an automobile that has born sensors to warning the driver when tire pressure is low or any other natural or man-made object that tin be assigned an Internet Protocol (IP) address and is able to transfer information over a network.
Increasingly, organizations in a diversity of industries are using IoT to operate more than efficiently, improve understand customers to evangelize enhanced customer service, improve decision-making and increase the value of the business concern.
How does IoT work?
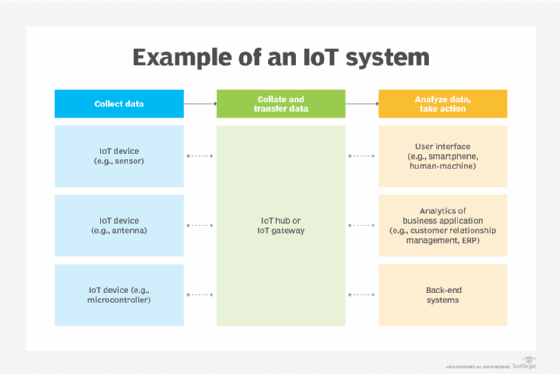
An IoT ecosystem consists of spider web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems, such as processors, sensors and advice hardware, to collect, transport and act on data they learn from their environments. IoT devices share the sensor data they collect by connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge device where data is either sent to the cloud to be analyzed or analyzed locally. Sometimes, these devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they go from one another. The devices do most of the piece of work without human intervention, although people tin can interact with the devices -- for instance, to gear up them up, give them instructions or access the data.
The connectivity, networking and communication protocols used with these web-enabled devices largely depend on the specific IoT applications deployed.
IoT tin also make use of artificial intelligence (AI) and car learning to aid in making data collecting processes easier and more dynamic.
Why is IoT of import?
The net of things helps people live and work smarter, likewise as gain complete control over their lives. In addition to offering smart devices to automate homes, IoT is essential to concern. IoT provides businesses with a real-time look into how their systems really piece of work, delivering insights into everything from the performance of machines to supply chain and logistics operations.
IoT enables companies to automate processes and reduce labor costs. It too cuts down on waste and improves service commitment, making information technology less expensive to industry and evangelize goods, as well every bit offering transparency into customer transactions.
Equally such, IoT is one of the most of import technologies of everyday life, and it will continue to pick up steam as more businesses realize the potential of connected devices to keep them competitive.
What are the benefits of IoT to organizations?
The internet of things offers several benefits to organizations. Some benefits are manufacture-specific, and some are applicative across multiple industries. Some of the common benefits of IoT enable businesses to:
- monitor their overall business processes;
- improve the customer experience (CX);
- save time and money;
- enhance employee productivity;
- integrate and adapt business models;
- make better business organization decisions; and
- generate more revenue.
IoT encourages companies to rethink the ways they arroyo their businesses and gives them the tools to ameliorate their business strategies.
Generally, IoT is about abundant in manufacturing, transportation and utility organizations, making use of sensors and other IoT devices; nevertheless, it has also found apply cases for organizations within the agriculture, infrastructure and domicile automation industries, leading some organizations toward digital transformation.
IoT can benefit farmers in agriculture past making their job easier. Sensors can collect data on rainfall, humidity, temperature and soil content, as well every bit other factors, that would help automate farming techniques.
The ability to monitor operations surrounding infrastructure is also a factor that IoT can help with. Sensors, for case, could be used to monitor events or changes within structural buildings, bridges and other infrastructure. This brings benefits with it, such as cost saving, saved time, quality-of-life workflow changes and paperless workflow.
A habitation automation business concern can utilize IoT to monitor and dispense mechanical and electrical systems in a building. On a broader scale, smart cities tin can aid citizens reduce waste and energy consumption.
IoT touches every manufacture, including businesses within healthcare, finance, retail and manufacturing.
What are the pros and cons of IoT?
Some of the advantages of IoT include the following:
- power to access data from anywhere at any fourth dimension on any device;
- improved advice between continued electronic devices;
- transferring data packets over a connected network saving time and money; and
- automating tasks helping to improve the quality of a business organisation's services and reducing the need for homo intervention.
Some disadvantages of IoT include the following:
- Equally the number of connected devices increases and more than information is shared between devices, the potential that a hacker could steal confidential information also increases.
- Enterprises may eventually have to deal with massive numbers -- maybe even millions -- of IoT devices, and collecting and managing the data from all those devices will be challenging.
- If there'due south a issues in the system, it's likely that every connected device will become corrupted.
- Since there's no international standard of compatibility for IoT, information technology'due south difficult for devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other.
IoT standards and frameworks
At that place are several emerging IoT standards, including the post-obit:
- IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks (6LoWPAN) is an open standard defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The 6LoWPAN standard enables any low-ability radio to communicate to the internet, including 804.fifteen.iv, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Z-Wave (for home automation).
- ZigBee is a low-power, low-data rate wireless network used mainly in industrial settings. ZigBee is based on the Establish of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.15.4 standard. The ZigBee Alliance created Dotdot, the universal language for IoT that enables smart objects to work securely on any network and understand each other.
- LiteOS is a Unix-similar operating system (Os) for wireless sensor networks. LiteOS supports smartphones, wearables, intelligent manufacturing applications, smart homes and the internet of vehicles (IoV). The Bone also serves as a smart device development platform.
- OneM2M is a machine-to-automobile service layer that can be embedded in software and hardware to connect devices. The global standardization torso, OneM2M, was created to develop reusable standards to enable IoT applications beyond different verticals to communicate.
- Information Distribution Service (DDS) was adult past the Object Direction Group (OMG) and is an IoT standard for real-fourth dimension, scalable and high-functioning M2M communication.
- Avant-garde Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) is an open source published standard for asynchronous messaging by wire. AMQP enables encrypted and interoperable messaging between organizations and applications. The protocol is used in client-server messaging and in IoT device management.
- Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) is a protocol designed by the IETF that specifies how low-power, compute-constrained devices can operate in the internet of things.
- Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) is a protocol for WANs designed to support huge networks, such as smart cities, with millions of low-ability devices.
IoT frameworks include the following:
- Amazon Spider web Services (AWS) IoT is a cloud computing platform for IoT released by Amazon. This framework is designed to enable smart devices to easily connect and securely interact with the AWS cloud and other connected devices.
- Arm Mbed IoT is a platform to develop apps for IoT based on Arm microcontrollers. The goal of the Arm Mbed IoT platform is to provide a scalable, connected and secure environment for IoT devices by integrating Mbed tools and services.
- Microsoft'southward Azure IoT Suite is a platform that consists of a set of services that enables users to interact with and receive data from their IoT devices, as well as perform diverse operations over data, such as multidimensional analysis, transformation and aggregation, and visualize those operations in a way that's suitable for business.
- Google's Brillo/Weave is a platform for the rapid implementation of IoT applications. The platform consists of two main backbones: Brillo, an Android-based Os for the development of embedded low-power devices, and Weave, an IoT-oriented communication protocol that serves every bit the communication language between the device and the cloud.
- Calvin is an open up source IoT platform released by Ericsson designed for building and managing distributed applications that enable devices to talk to each other. Calvin includes a development framework for application developers, as well as a runtime surround for handling the running awarding.
Consumer and enterprise IoT applications
In that location are numerous real-world applications of the internet of things, ranging from consumer IoT and enterprise IoT to manufacturing and industrial IoT (IIoT). IoT applications span numerous verticals, including automotive, telecom and free energy.
In the consumer segment, for instance, smart homes that are equipped with smart thermostats, smart appliances and connected heating, lighting and electronic devices can be controlled remotely via computers and smartphones.
Article of clothing devices with sensors and software can collect and analyze user data, sending messages to other technologies well-nigh the users with the aim of making users' lives easier and more comfortable. Vesture devices are besides used for public safety -- for instance, improving first responders' response times during emergencies by providing optimized routes to a location or past tracking construction workers' or firefighters' vital signs at life-threatening sites.
In healthcare, IoT offers many benefits, including the ability to monitor patients more closely using an assay of the information that'due south generated. Hospitals often use IoT systems to complete tasks such as inventory management for both pharmaceuticals and medical instruments.
Smart buildings tin can, for instance, reduce energy costs using sensors that detect how many occupants are in a room. The temperature can adjust automatically -- for instance, turning the air conditioner on if sensors discover a conference room is total or turning the heat down if anybody in the role has gone abode.
In agriculture, IoT-based smart farming systems can assistance monitor, for example, low-cal, temperature, humidity and soil moisture of crop fields using connected sensors. IoT is also instrumental in automating irrigation systems.
In a smart city, IoT sensors and deployments, such every bit smart streetlights and smart meters, can help convalesce traffic, conserve energy, monitor and address environmental concerns, and amend sanitation.
IoT security and privacy issues
The internet of things connects billions of devices to the cyberspace and involves the apply of billions of data points, all of which demand to be secured. Due to its expanded attack surface, IoT security and IoT privacy are cited as major concerns.
In 2016, 1 of the well-nigh notorious contempo IoT attacks was Mirai, a botnet that infiltrated domain name server provider Dyn and took down many websites for an extended period of time in one of the biggest distributed deprival-of-service (DDoS) attacks ever seen. Attackers gained access to the network by exploiting poorly secured IoT devices.
Because IoT devices are closely connected, all a hacker has to do is exploit ane vulnerability to manipulate all the data, rendering information technology unusable. Manufacturers that don't update their devices regularly -- or at all -- leave them vulnerable to cybercriminals.
Additionally, continued devices frequently ask users to input their personal data, including names, ages, addresses, telephone numbers and fifty-fifty social media accounts -- information that's invaluable to hackers.
Hackers aren't the only threat to the cyberspace of things; privacy is another major concern for IoT users. For instance, companies that brand and distribute consumer IoT devices could utilise those devices to obtain and sell users' personal data.
Beyond leaking personal information, IoT poses a risk to disquisitional infrastructure, including electricity, transportation and inancial services.
What is the history of IoT?
Kevin Ashton, co-founder of the Machine-ID Center at the Massachusetts Plant of Technology (MIT), start mentioned the internet of things in a presentation he made to Procter &Take chances (P&Chiliad) in 1999. Wanting to bring radio frequency ID (RFID) to the attending of P&G's senior management, Ashton called his presentation "Net of Things" to contain the cool new trend of 1999: the net. MIT professor Neil Gershenfeld'south book, When Things First to Remember, as well appeared in 1999. Information technology didn't utilise the exact term but provided a clear vision of where IoT was headed.
IoT has evolved from the convergence of wireless technologies, microelectromechanical systems (MEMSes), microservices and the net. The convergence has helped tear downwardly the silos between operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT), enabling unstructured machine-generated data to be analyzed for insights to drive improvements.
Although Ashton's was the first mention of the internet of things, the idea of connected devices has been around since the 1970s, under the monikers embedded internet and pervasive computing.
The commencement internet appliance, for example, was a Coke motorcar at Carnegie Mellon University in the early on 1980s. Using the web, programmers could check the status of the auto and decide whether there would be a cold drink awaiting them, should they decide to make the trip to the machine.
IoT evolved from M2M communication, i.e., machines connecting to each other via a network without human interaction. M2M refers to connecting a device to the cloud, managing it and collecting data.
Taking M2M to the adjacent level, IoT is a sensor network of billions of smart devices that connect people, systems and other applications to collect and share information. As its foundation, M2M offers the connectivity that enables IoT.
The net of things is also a natural extension of supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA), a category of software application programs for process control, the gathering of data in existent fourth dimension from remote locations to control equipment and conditions. SCADA systems include hardware and software components. The hardware gathers and feeds information into a computer that has SCADA software installed, where it is so processed and presented in a timely manner. The development of SCADA is such that belatedly-generation SCADA systems developed into kickoff-generation IoT systems.
The concept of the IoT ecosystem, however, didn't really come into its own until the middle of 2010 when, in role, the government of Cathay said it would make IoT a strategic priority in its five-year plan.
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/iotagenda/definition/Internet-of-Things-IoT
0 Response to "house has multible steps, whats best way to carry items up"
Yorum Gönder